- Understand types of problems
- Learn about the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals
- Identify different communities you belong to
- Begin documenting your community’s needs
- Brainstorm problems you’d like to solve in your community

Your first step!
Finding a problem to solve

Ideation
It is one of the hardest parts of the Technovation project!

Problem First
Focus on finding the problem. Don't start with a solution!
START WITH COMMUNITIES
One strategy for coming up with problems is to start is with your community.

We all belong to or are a part of groups, such as our school peers or sports teams.
Many groups are also communities.
A community is a group of people who have something in common. A community could be
the people who live in the same place or
a group that shares similar interests.
You may be surprised by how many communities you belong to!
COMMUNITIES ARE BASED ON DIFFERENT THINGS
People who go to the same school, or who live in the same city or country

People who enjoy the same hobbies, like playing on the same sports team or playing the same online games
People who identify as a certain race, ethnicity, or gender

People who follow the same religion

Stop
and
Discuss
Can you name some other types of communities?


Identify your community’s needs.
Look at the world around you and observe your community closely.
Your observations and evidence will later help support your team’s eventual solution, and how it effectively solves your community’s needs.
Let’s start with …
How well do you know your community?
The next two activities will help you become more aware of the communities you belong to, and the problems they might face.
ACTIVITY 1: UNDERSTANDING YOUR COMMUNITY
Follow the instructions in worksheet (Page 1) to
ACTIVITY 2: UNDERSTANDING YOUR COMMUNITY
Follow the instructions in worksheet (Page 2) to
PUTTING PROBLEMS IN CATEGORIES
As you identify problems you might want to solve, it helps to categorize them.
One way to categorize them is by looking at the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
This can help you understand underlying issues and direct you towards research for your problem.

U.N. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are 17 goals that the United Nations has agreed are important to solve. They include 5 main areas:
Basic human needs and rights
such as water, food, sleep, clothing, shelter, good education

Environment
such as climate action, access to clean water, renewable energy
Safety needs
such as health, well-being, safety against accidents and illness

Social needs
such as friendships, family, acceptance by others, respect, productivity

Individual action
such as equality, peace, and justice
Here is the full list of the 17 goals

ACTIVITY 3: CATEGORIZING PROBLEMS
Follow the instructions in worksheet (Page 1) to
BRAINSTORMING
After observing your community, you might have identified some good problems you want to work on, or you might still be uncertain. So, let’s try to think of more problems you can tackle, by brainstorming.
Brainstorming is a group activity that is meant to generate a large number of ideas. As you brainstorm you might feel vulnerable as you contribute different ideas. This is normal!

BRAINSTORMING TIPS
Click on the wheels inside the gears below to learn a tip!

Be sure to capture all ideas, even wild ones!
No judgement, on other people's ideas, or on your own!
Build off each other's ideas.
One conversation at a time - don't cut each other off.
Be visual - you can draw instead of writing words.
Go for as many ideas as you can.
Stay focused.
HOW NOT TO BRAINSTORM
Here is a video that shows examples of less effective ways to go about brainstorming, and more effective ways, so you can better understand this process
There are many different ways to brainstorm. Some examples are below. Do what makes sense for your team.
Using paper, post-it notes, or an online tool like Jamboard, write down as many ideas as you can. The more the better. Watch the video below for a great example of group brainstorming.
ACTIVITY 4: BRAINSTORMING PROBLEMS
Using your brainstorming strategy, follow the instructions in worksheet (Page 2) to
ACTIVITY 5: CATEGORIZING PROBLEMS
Follow the instructions in worksheet (Page 3) to
Mentor Tip
Best practices: When identifying problems, start by thinking about relatable scenarios that are encountered daily. For example, “Imagine you’re trying to use your favorite app, but it keeps crashing. Identifying the problem is the first step to fixing it.” This helps students understand the importance of problem identification in a context they are familiar with.
In discussion, it’s natural for teams to name solutions and problems to solve. As a Mentor, it’s important thing to keep your teams from solution jumping or proposing a solution before fully understanding a problem.
Keeping a separate list of solutions to track them as they come up gives the team something they can reference later, but always guide them back to thinking of problems. For example “That’s a great idea for a solution we’ll write down on the solution list. Let’s keep thinking of problems we can solve and what may be causing the problem.”
Don’t rush the process of thinking of problems and understanding them. Asking “why?” will help get down to the root cause of a problem, and that’s what you want to solve.
These videos will help students understand how to identify problems in various contexts and relate those skills to both everyday experiences and their coding projects.
Encourage teams to write down all their ideas as they think of problems to solve. Having this archive of ideas can help if they decide to shift their focus later in the season.
Guiding Questions to ask students:
Can you think of a time when you were unable to complete a task? What did you do to try to fix it?
Can you think of concerned you’ve heard from people in your community?
Why do you think it’s important to identify a problem before trying to solve it?
How can you use what you learn in coding to solve real-life problems?
Mentor tips are provided by support from AmeriCorps.

REFLECTION
This lesson took A LOT of thought and work.
Hopefully it has sparked some ideas for you.
Ask yourself these questions:

REVIEW OF KEY TERMS
- Ideation – The process of coming up with ideas
- Sustainable Development Goals – The United Nations’ commitments to reduce poverty and help the environment
- Brainstorming – A way to think of a lot of ideas quickly
- Community – A group of people who have something in common
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
App Gallery
You might want to check out what Technovation Girls teams have done in the past. Here are the steps to find pitch videos from past Technovation Girls teams:
- Visit the Technovation App Gallery
- Choose a topic from the dropdown that matches the category your problem falls in
- Filter by location, year, and division
- Click Apply Filters
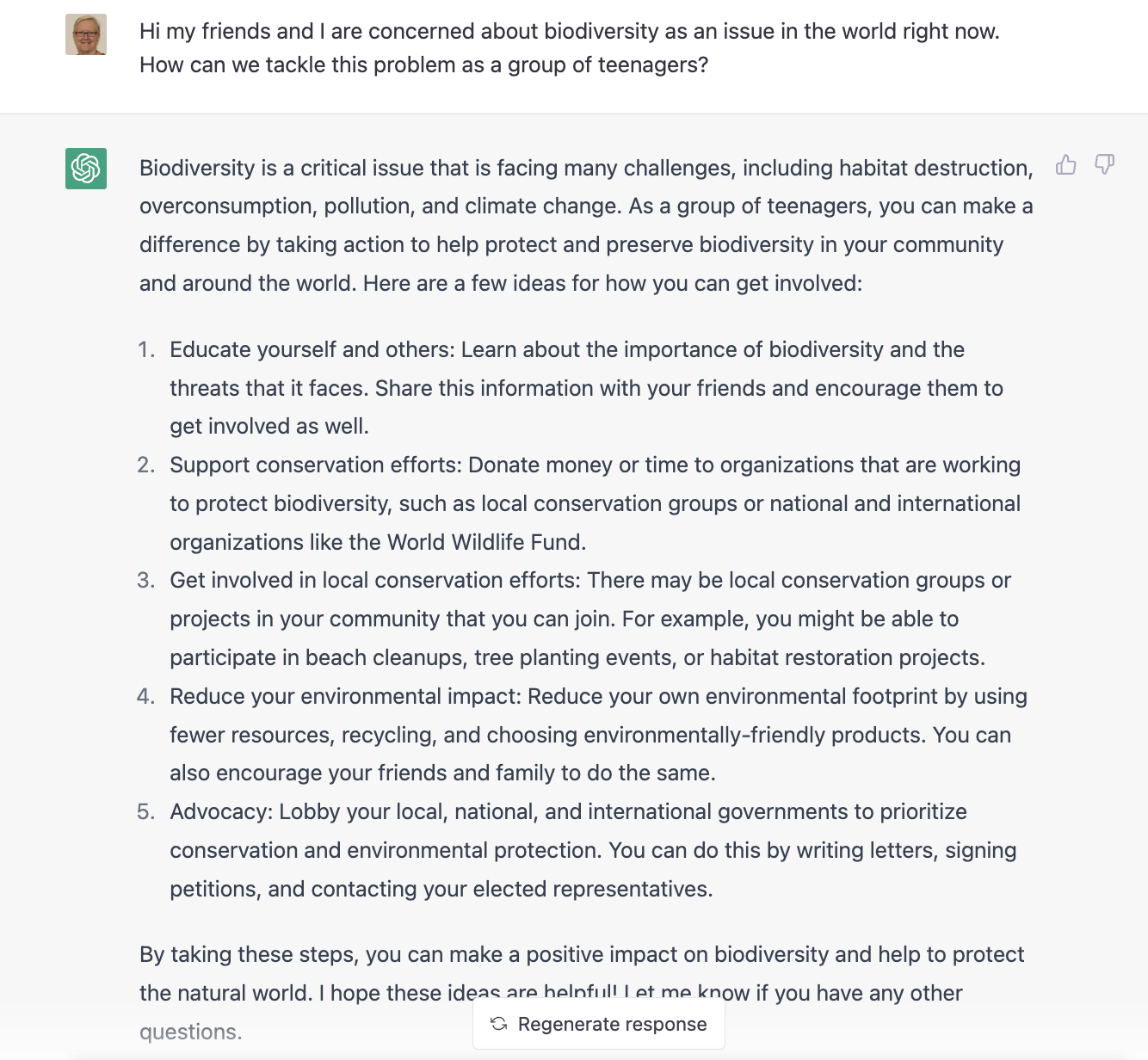
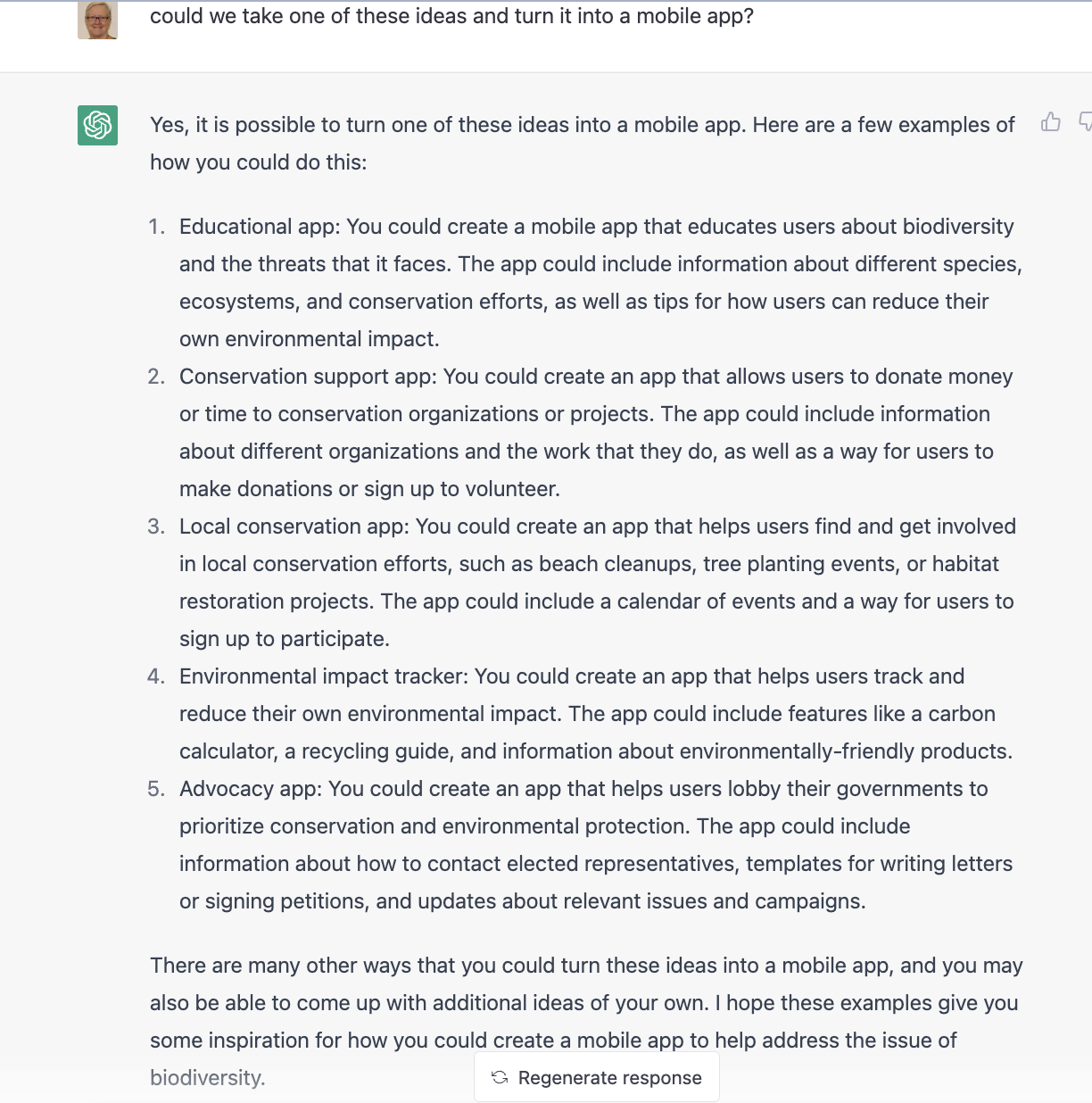
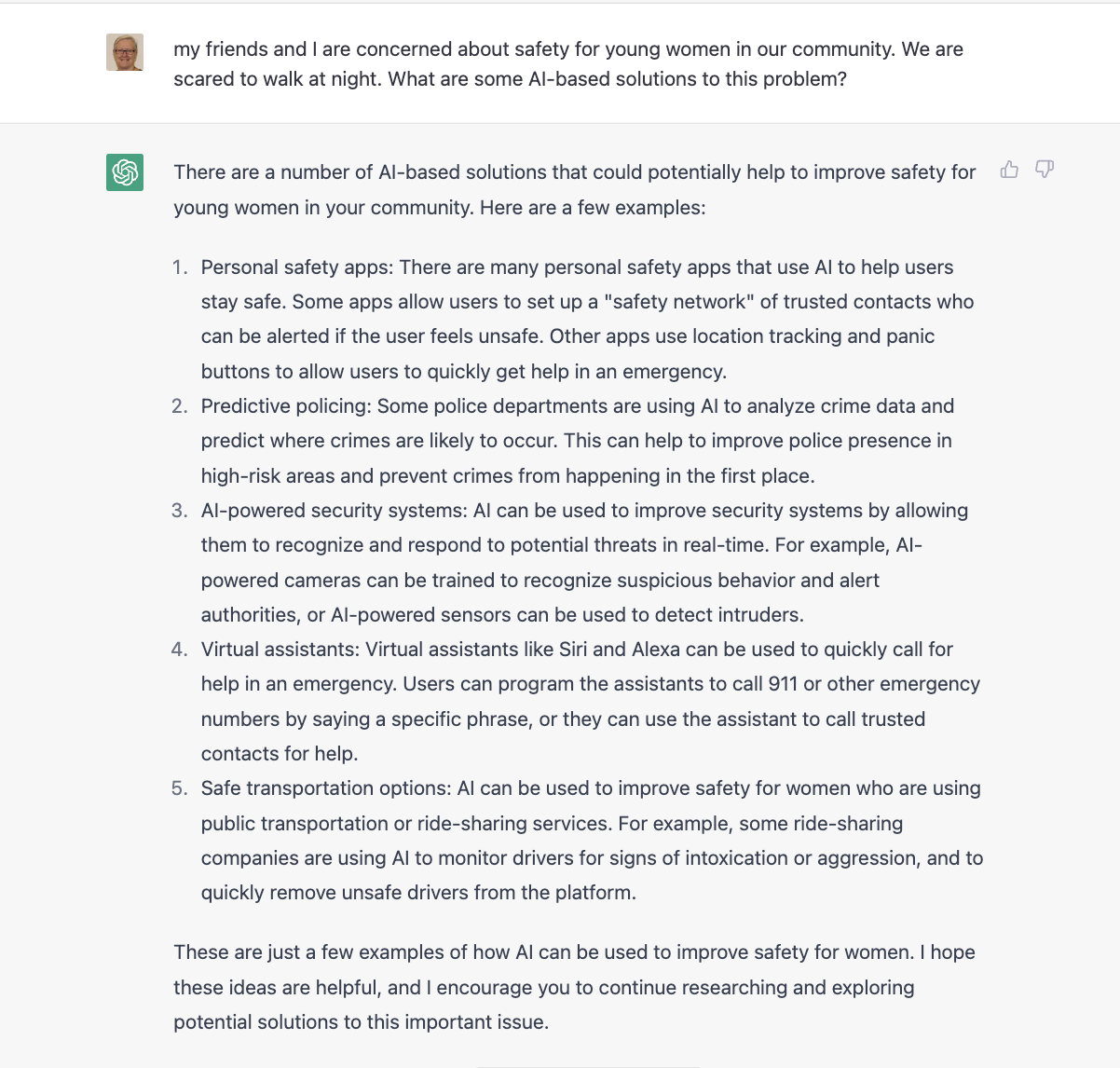
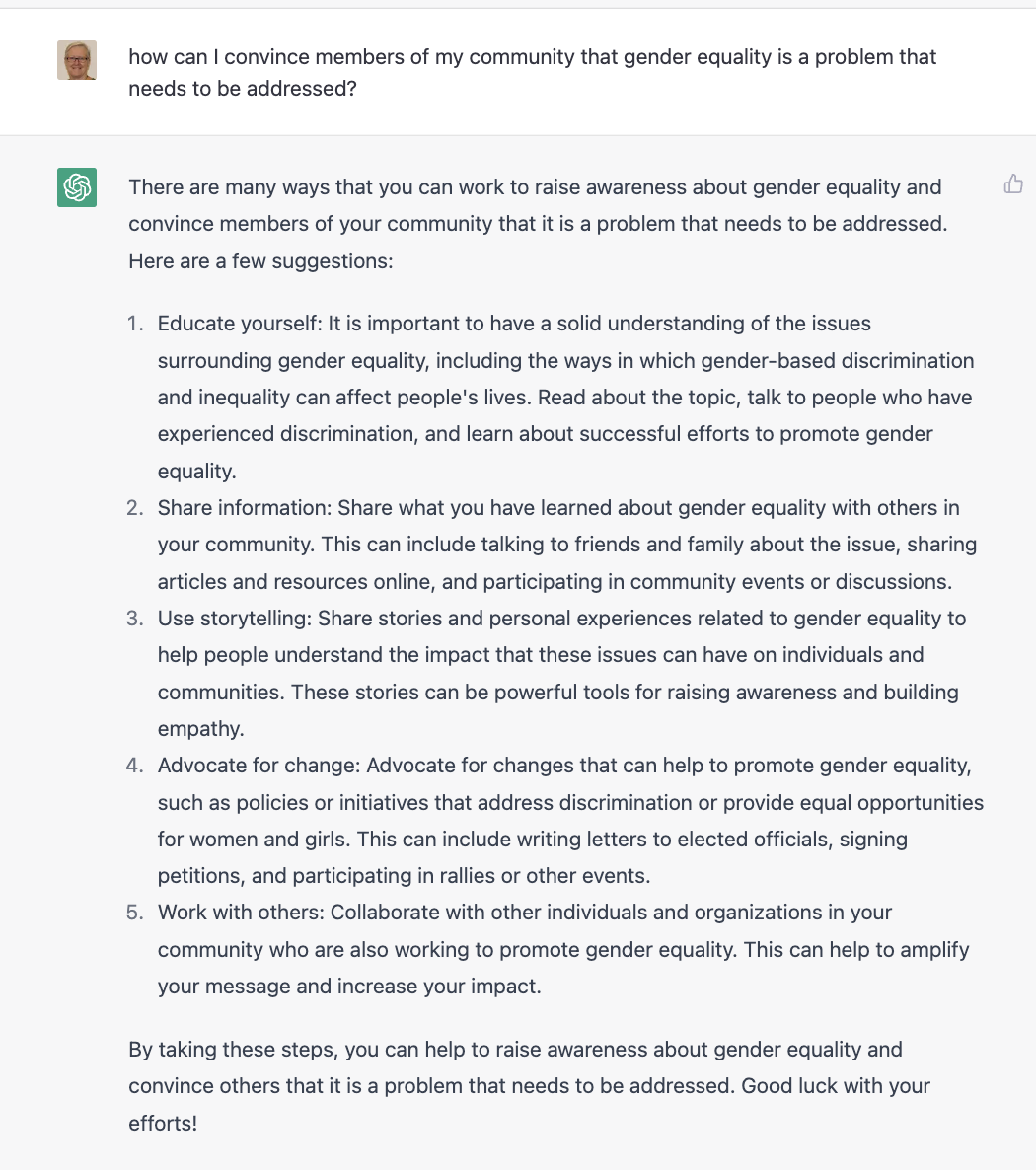
ChatGPT
Another exciting tool that can help you identify a problem is ChatpGPT, from OpenAI.
You can sign up for a free account that will give you enough free credit to work on your Technovation project.
Click the toggles below to see some examples prompts using ChatGPT for Technovation ideation.
Note that responses are AI-generated, so not necessarily factual or complete. Use of ChatGPT is recommended as another resource of many in the ideation process. It may help generate some some ideas your team can expand on and use as a launchpad for other ideas.
Don’t get discouraged if you haven’t got a solid problem locked down yet. It can take several meetings and discussions to decide on a problem you all care about and want to work together to solve. Listen to past participants in this video!