- Review different components you can use in App Inventor or Thunkable
- Find one component that can help your app
- Research a tutorial and code at least one component into your app
These are the activities for this lesson:
SMARTPHONE COMPONENTS
It’s time to choose and code the components, some of which include sensors, that you want your app to use. The various components available will allow your app to do many different things – be sure to choose the ones that are right for you!
This lesson is a reference for you to learn about many components you can use in your app.
You probably have chosen your platform by now, but we’ll list all the components for both App Inventor and Thunkable, just so you can be aware of available components.
Look for the components that you can use to implement the features you have planned for your app.
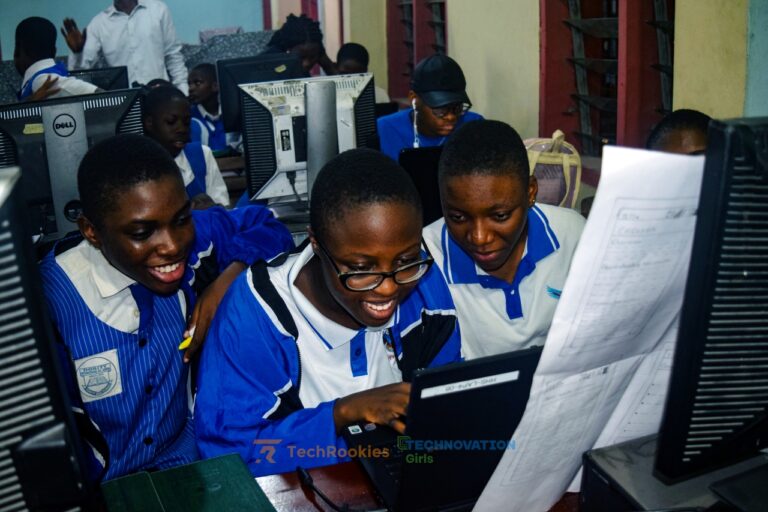

COMPONENT LIST BY CATEGORY
The components that follow are ones beyond the standard User Interface components, that allow the user to interact with the app.
This is not a complete list, but does cover most of the currently available components. Thunkable and App Inventor continue to add more features and components all the time.
The information below is also available in this document.
| Feature Description | App Inventor | Thunkable |
|---|---|---|
| Allows the user to take videos. You can use it for social apps, video sharing apps, or anytime else that you would want your user to record a video. | Camcorder | Camera |
| Allows the user to take pictures. This can be useful for apps that allow users to set profile pictures or take pictures to share or save to a gallery. | Camera | Camera |
| Allows the user to pick an image from their photo library. It will allow users to pick photos that they have taken outside of using your app. | ImagePicker | Files (photo library) |
| Allows you to embed a video into the app that the user can click on. The video must be a .wmv, .3gp or .mp4 and not be bigger than 1MB. | VideoPlayer | Video |
| Allows you to translate text into another language. It requires that your app has internet access since it relies on external translation services. | Translator | Speech |
| Allows a user to record a sound or noise. | SoundRecorder | Sound |
| This audio component plays a sound. This works best for “long” sounds, such as songs, speeches, or poems. Thunkable has just one component, Sound, for any length audio. | Player | Sound |
| Very similar to the Player component, but is best for short sounds, like notification “dings”. | Sound | Sound |
| Translates the user’s speech into text. This is especially useful for apps that require hands-free capabilities. | SpeechRecognizer | Speech |
| This component does the reverse of SpeechRecorder; it allows users to enter text and the app will read it out loud. | TextToSpeech | Speech |
| You can make a JSON animation play in your app. | Not available | Animation |
| Feature Description | App Inventor | Thunkable |
|---|---|---|
| Displays the user’s contacts and allows users to choose someone from that list. | ContactPicker | Not available |
| Allows the user to input an email address from the user’s contact list. | EmailPicker | Not available |
| Allows the user to pick a phone number from a phone contact list. | PhoneNumberPicker | Not available |
| Allows you to embed a video into the app that the user can click on. The video must be a .wmv, .3gp or .mp4 and not be bigger than 1MB. | VideoPlayer | Video |
| Enables the user to make a phone call from your app. | PhoneCall | Share |
| Allows the user to send a text message to another user’s phone through your app. | Texting | Share |
| This audio component plays a sound. This works best for “long” sounds, such as songs, speeches, or poems. Thunkable has just one component, Sound, for any length audio. | Player | Sound |
| Allows users to share messages, images, or other content in your app with other apps on the user’s phone, like email and messaging. | Sharing | Share |
| Allows communication between your app and Twitter. Users can search for tweets, send and receive messages, get a list of followers, and more. | Not available | |
| Thunkable allows you to add ads to your app. All apps must be first approved by Thunkable before they can be downloaded or published. | Not available | Ads |
| Feature Description | App Inventor | Thunkable |
|---|---|---|
| Allows your app to start up other apps, like Camera or Google Maps, or user-created apps installed on phone. | ActivityStarter | Open link (Control block) |
| Allows you to embed a map into your app. App Inventor includes components like Markers and Shapes that can be added to a map. These features are added in code in Thunkable. | Maps | Maps |
| Allows users to view web pages within your app. | WebViewer | Web Viewer |
| Enables your app to send and get information to and from external websites. | Web | Web API |
| Enables the user to make a phone call from your app. | PhoneCall | Share |
| These components enable your app to connect with Bluetooth devices. | Bluetooth Client, Bluetooth Server, BlueToothLE (extension) | Bluetooth Low Energy |
| This audio component plays a sound. This works best for “long” sounds, such as songs, speeches, or poems. Thunkable has just one component, Sound, for any length audio. | Player | Sound |
| Used to collect data from external sources (sensors, web, data files) and display them in chart form. | Chart, ChartData2D | Not available |
| Can be used to connect to serial devices like Arduino. | Serial | Not available |
| Allows users of your app to sign up with a username and password. This requires you first set up a Firebase account. | Not available | Sign-in |
| Allow you to embed a pdf file within your app | Not available | PDF Reader |
| Feature Description | App Inventor | Thunkable |
|---|---|---|
| Can determine if the phone is shaking and if it’s being held upright or upside-down. This capability is very useful when you want the screen to reorient in response to how the phone is being held, or if you want the app to react to shaking. | AccelerometerSensor | Accelerometer |
| Uses the accelerometer sensor to measure how many steps the user holding the phone takes, and can also estimate distance traveled. | Pedometer | Not available |
| Can sense if the phone is being tilted. It is more precise than the accelerometer and can measure how much the orientation of the phone has changed. | GyroscopeSensor | Gyroscope |
| Used to measure magnetic flux density. Not all phones support this capability. | MagneticFieldSensor | Magnetometer |
| Allows your app to get the current time or use a timer. This can be useful for setting a timed alarm or using a timer. | Clock | Timer |
| Collects the latitude and longitude of the phone’s location. This sensor can be useful anytime you need to search for points of interest near the user. | LocationSensor | Location Sensor |
| Tells if the phone is in close proximity to an object. It is often used to tell if the user has the phone close to their ear. Not all phones can support this capability. | ProximitySensor | Not availalbe |
| Allows your app to read a barcode. | BarcodeScanner | Camera |
| Measures the ambient air pressure. | Barometer | Not available |
| Measures the relative ambient air humidity. Uncommon for most mobile devices. | Hygrometer | Not available |
| Measures the light level. | LightSensor | Not available |
| Allows your app to share data with other NFC (Near-field Communication) -equipped devices. | NearField | Not available |
| Provides information about the device’s physical orientation in three dimensions: roll, pitch, and azimuth. | OrientationSensor | Not available |
| Measures the ambient (external) temperature. | Thermometer | Not available |
| Feature Description | App Inventor | Thunkable |
|---|---|---|
| Block that lets you update and store information within the app. Any information is erased when the app is closed. | Variable | app Variable |
| Allows your app to store and update information locally on the mobile device and use it within the app. Data can be stored and retrieved between runs of the app. In Thunkable, DataViewer and DataViewerGrid can store data locally using the “Create your own Table” option. | TinyDB | stored Variable DataViewer List Data Viewer Grid |
| Allows your app to store, retrieve, and update data in the cloud so data can be shared between different users of the app. Thunkable offers cloud variables using Firebase. DataViewer and DataViewerGrid can be linked to Airtable, Google Sheets, and Webflow. App Inventor’s Spreadsheet component links to Google Sheets. | CloudDB FirebaseDB Spreadsheet | cloud Variable – (Firebase) DataViewer List DataViewerGrid |
| Feature Description | App Inventor | Thunkable |
|---|---|---|
| Allows communication with an AI chat bot, OpenAI’s ChatGPT. | Chatbot | Open AI Services (text completion) |
| Allows you to include DALL-E in your app to create and edit images. | Imagebot | Open AI services (image generation) |
| Allows you to create your own machine learning model (image, sound, pose) and use it in your app. | PersonalImageClassifier PersonalAudioClassifier PoseNetExtension TeachableMachine (note these all require you to add the extension) | Not available |
| Feature Description | App Inventor | Thunkable |
|---|---|---|
| Adds an area on the screen where users can draw. This is also where you can add sprites that you can animate. | Canvas | Canvas |
| These components are the elements that can be animated and interacted with inside a game or animation | ImageSprite Ball |
Sprite |
You will add components in the Designer window of App Inventor. You will have to click on a category in the palette to open the drawer to show the components.
ACTIVITY: LEARN A NEW COMPONENT
Choose a component to learn about
- Choose at least one component or sensor that you think you will use in your app.
- Find documentation and/or a tutorial to use the component in an app. You can start here:
- Code an app using that new component
Mentor Tip
Best practices: The component that you pick does not have to be perfect for your app! As long as you are learning about a new component, that is what matters. Just pick something you think might work and if you figure out it doesn’t work that’s okay. In the coding world we call this research a “spike” because you are trying to quickly dig as deep as possible (kind of like hitting a railroad spike into the ground).
Guiding Questions to ask students: If we were making an app for an Apple watch, what kind of components might be on the apple watch? (Heart rate monitor, gyroscope – for step tracking, bluetooth). How much data are you collecting? Could you use that data to train your AI model?
Mentor tips are provided by support from AmeriCorps.

One of the best skills you can learn as a programmer is how to find resources to help you when you are stuck or need to learn how to use something.
This activity is practice!
It may not exactly align with the app you want to build, but practicing coding with components will help when you come to build your own app.
REFLECTION
This lesson is a reference for all of the components you can use to build your app. Finding a tutorial or documentation to learn how to use your component is not easy!

REVIEW OF KEY TERMS
- User Interface Components – standard components a user would interact with like buttons, labels, and text boxes
- Media Components – examples of media components are photos, audio, and video.
- Sensors – different types of devices installed on a phone that gathers data for various purposes
- Social Components – features that enable users to make phone calls, send emails, text and share things through your app
- Connectivity Components – features that allow your app to interact with places outside of your app, like the web and other apps
- Storage Components – blocks and components that allow you to store information in the app, on the device, and in the cloud
- AI Components – components that allow you to use machine learning models or generative AI tools within your app
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
Other helpful tutorial sites for App Inventor:
- appinventor.org
- The Coding Bus beginner course (many component tutorials)
- GirlsCodeIt Technovation tutorials
- Full Component Reference List (Google doc for printing)


